Antioxidants are an anti-influenza virus infection therapy.
Notes by Marshall Thurber
Influenza A virus is one of the major causes of respiratory disease pathogens with characteristics of high morbidity and mortality
Morbidity is a term used to describe how often a disease occurs in a specific area. It is the rate of disease or proportion of diseased persons in a given locality, nation, etc. An example of morbidity is the number of people who have cancer in a given country compared to its entire population.
Currently, effective treatments are still inadequate because of current anti-viral drugs resistance and vaccine escape, especially against the highly pathogenic influenza virus. Thus, it is urgent need to develop new antiviral approaches.
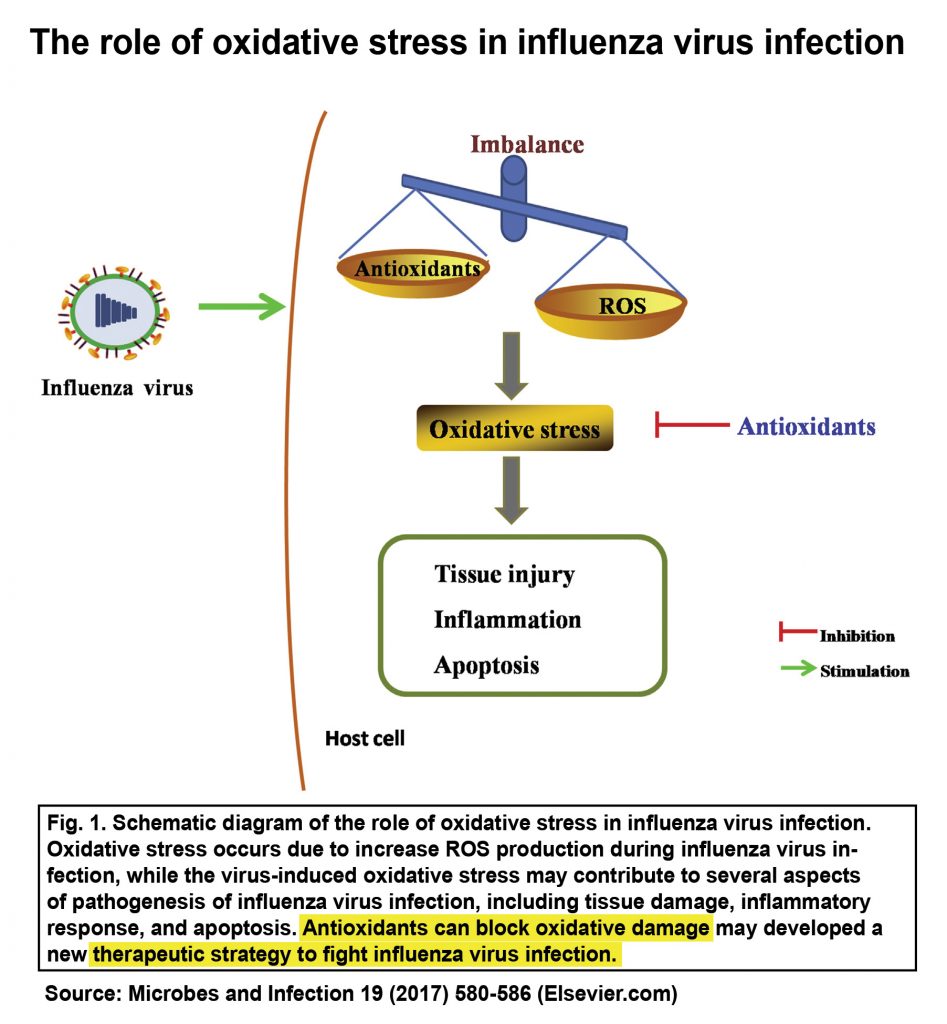
1. Introduction The role of oxidative stress in influenza virus infection. Institut Pasteur Microbes and Infection 2017 pp 580—586)
The influenza virus is dependent on affecting host cell functions to promote its replication. A virus wants to hijack the host cell functions to enhance itself replication.
2.2. Excessive accumulation; The role of oxidative stress in influenza virus infection. Institut Pasteur Microbes and Infection 2017 pp 580—586).
Virus invasion seems to cause oxidative stress, resulting in inflammatory damage. The is an excessively exaggerated immune response, commonly known as cytokine storm.
A cytokine storm is an overproduction of immune cells and their activating compounds (cytokines). In a flu infection it is associated with a surge of activated immune cells into the lungs. High levels of free radicals (ROS) promote a pathological inflammatory response. Oxidative-stress is used to explain the mechanism of influenza virus-induced immunopathology.
2.3. Virus-induced inflammation; The role of oxidative stress in influenza virus infection. Institut Pasteur Microbes and Infection 2017 pp 580—586)
Cell apoptosis is also named programmed cell in host cells. Mitochondria cell self-destruction cascade happens when free radicals (ROS) are too plentiful. When there are too many free radicals they play a critical role in the mitochondria cell self-destruction cascade.
2.4. The relationship between oxidative stress and apoptosis: The role of oxidative stress in influenza virus infecti on. Institut Pasteur Microbes and Infection 2017 pp 580—586)
Protection of cells from injury during influenza infection is particularly important. It is the cellular antioxidation defense systems that protect cells. Oxidants (the opposite of antioxidants) are involved in influenza virus replication. The process of oxidative stress is activated by excessive free radicals (ROS) and the degree of this activation can be regulated by antioxidants.
3.Oxidative stress pathway: The role of oxidative stress in influenza. Microbes and Infection 2017 pp 580—586)
Small-molecule antioxidants work on influenza viruses. There is no antioxidant molecule smaller than a fullerene. To be bioactive Fullerenes must be free (no clumping). The only fully soluble (non-clumping) Fullerene is the Buckminster Fullerene offered by FullerLifeC60. It is so unique it has a patent pending.
4. Antioxidants in anti-influenza virus therapy. The role of oxidative stress in influenza. Microbes and Infection 2017 pp 580—586)
Antioxidants represent a therapeutic option to fight influenza. The importance of the development of novel compounds that block oxidative stress are needed.
5. Conclusion and prospective . The role of oxidative stress in influenza. Microbes and Infection 2017 pp 580—586)
The U.S. is already in influenza season. In the present season, there have been more than 22 million flu cases, 210,000 hospitalizations and 12,000 deaths – including 78 children – These facts are based on the weekly influenza report from the Centers for Disease Control.
Viruses like the flu can be deadly. Those who get very ill or die have weakened immune systems. Have the highest probability of staying healthy by making your immune system the strongest possible.