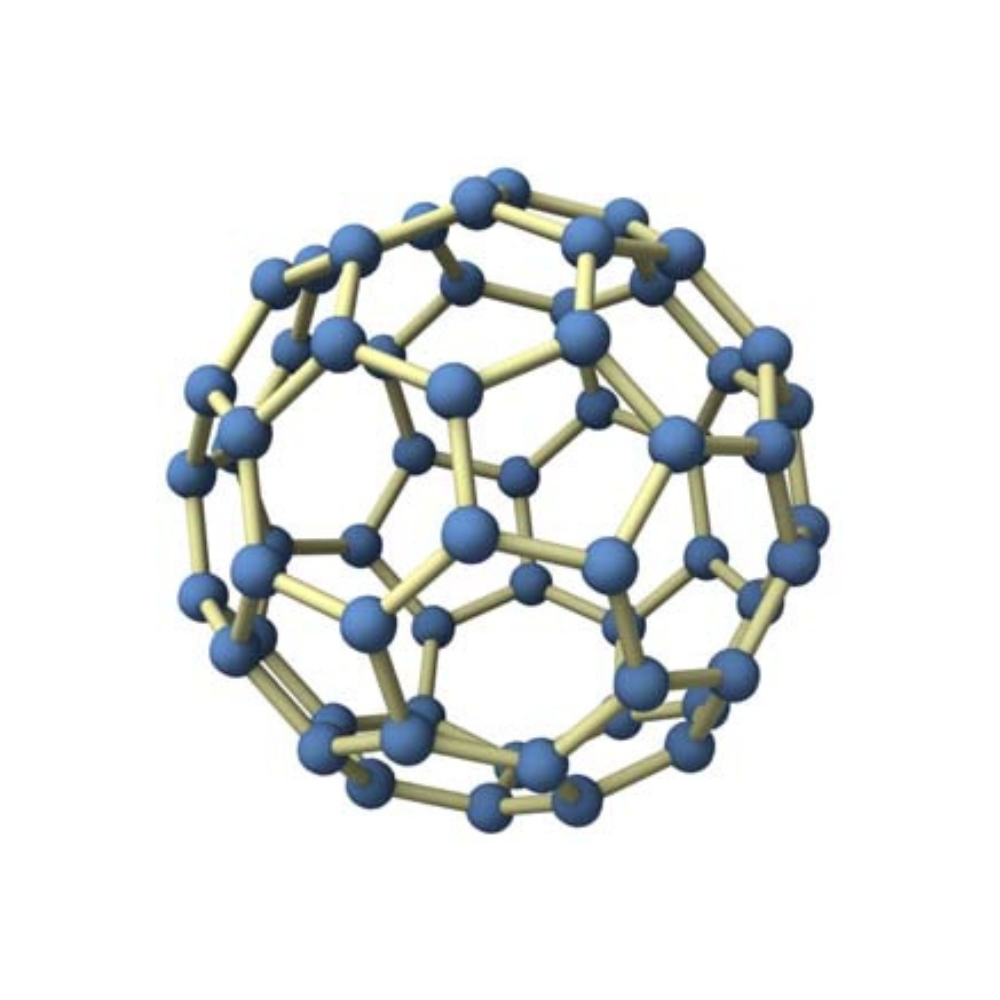
C60 Structure
C60, also known as Buckminsterfullerene or Buckyball, is a unique carbon molecule that consists of 60 carbon atoms arranged in a spherical shape. The structure of C60 is based on the geodesic dome, a structure that was popularized by architect and engineer Buckminster Fuller, hence the name Buckminsterfullerene.
The C60 molecule consists of 20 hexagons and 12 pentagons arranged in a pattern that resembles the lines of latitude and longitude on a globe. The hexagons form the flat surface of the sphere, while the pentagons are required to create the curvature of the structure. Each carbon atom in the C60 molecule is covalently bonded to three neighboring carbon atoms, forming a network of covalent bonds that creates a strong and stable molecule.
The diameter of the C60 molecule is approximately 0.7 nanometers, making it one of the largest molecules known. The unique structure of C60 gives it many interesting properties, such as its ability to act as a superconductor at low temperatures, and its potential as a drug delivery system due to its ability to enter cells and release drugs.
What is the significance of the unique structure of the C60 molecule?
The unique structure of the C60 molecule is significant because it gives rise to many interesting properties and potential applications in various fields. The spherical shape of the molecule is based on the geodesic dome structure, which provides a high degree of stability and strength. The covalent bonds between the carbon atoms are strong, which contributes to the stability of the molecule. The C60 molecule is also unique in its size, as it is one of the largest molecules known.
The unique properties of the C60 molecule make it a potential candidate for various applications, such as drug delivery systems, due to its ability to enter cells and release drugs. It is also being studied for its potential use in electronics and materials science, as it has properties such as high electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and photoconductivity. The C60 molecule also has potential applications in nanotechnology, where its unique properties can be harnessed to develop new materials and technologies.
Overall, the unique structure of the C60 molecule is significant because it provides a platform for the development of new technologies and materials that can have a significant impact on various fields, such as medicine, electronics, and materials science.
For more info see C60 Supercharged
What are the properties of the C60 molecule that make it a potential candidate for drug delivery systems?
The C60 molecule has several properties that make it a potential candidate for drug delivery systems. One of the most important properties is its ability to enter cells and cross biological membranes. The C60 molecule is small enough to pass through cell membranes and can potentially carry drugs into cells to treat various diseases.
The C60 molecule has a high surface area, which allows it to bind with molecules and potentially carry them to their target sites. The surface of the C60 molecule can be modified with functional groups that can help it target specific cells or tissues.
Another property of the C60 molecule that makes it attractive for drug delivery systems is its low toxicity. Studies have shown that the C60 molecule has low toxicity and is not harmful to cells or tissues in the body. This is an important property for drug delivery systems, as the carrier molecule should not cause harm to the body.
Moreover, the C60 molecule is stable and resistant to degradation, which allows it to protect drugs from being broken down or metabolized in the body before they reach their target site. It can also potentially prolong the release of drugs, resulting in longer-lasting therapeutic effects.
In conclusion, the unique properties of the C60 molecule, such as its ability to enter cells, high surface area, low toxicity, stability, and resistance to degradation, make it a promising candidate for drug delivery systems. Further research is needed to explore the full potential of C60-based drug delivery systems in treating various diseases.